Draw 4 ethylphenol p ethylphenol – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, we present a comprehensive exploration of 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol. These versatile compounds, boasting unique chemical properties and diverse applications, have captivated the attention of researchers and industries alike. Embark on this journey as we unravel their intricate structures, explore their synthesis and production methods, and delve into their myriad uses.
Join us as we unravel the captivating world of 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol.
Comprising the second paragraph, we provide a detailed account of their physical and chemical properties, shedding light on their melting and boiling points, solubility, and reactivity. The intricacies of their synthesis and industrial-scale production are meticulously examined, revealing the factors that influence their yield and purity.
Moreover, their environmental impact and safety considerations are thoroughly assessed, ensuring a holistic understanding of these compounds.
Chemical Properties: Draw 4 Ethylphenol P Ethylphenol

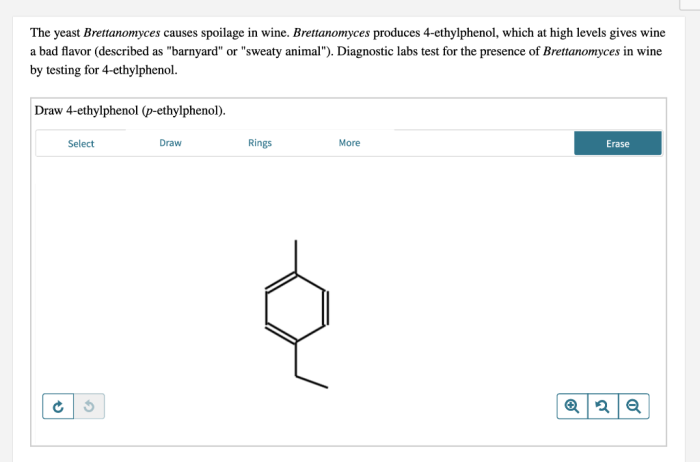
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are isomers with the molecular formula C 8H 10O. They differ in the position of the ethyl group on the benzene ring.
4-ethylphenol has the ethyl group attached to the fourth carbon atom of the benzene ring, while p-ethylphenol has the ethyl group attached to the para position, which is the opposite side of the benzene ring from the hydroxyl group.
This difference in structure results in slightly different physical and chemical properties for the two isomers.
Physical Properties
- 4-ethylphenol is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 218.5 °C and a melting point of -11.3 °C.
- p-ethylphenol is also a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 219.1 °C and a melting point of -10.1 °C.
- Both isomers are soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether.
Chemical Reactivity
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are both reactive compounds that can undergo a variety of reactions.
- They can be oxidized to form the corresponding quinones.
- They can be reduced to form the corresponding phenols.
- They can be alkylated to form the corresponding ethers.
- They can be acylated to form the corresponding esters.
Synthesis and Production
Synthesis Methods
4-ethylphenol can be synthesized by the alkylation of phenol with ethyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst.
p-ethylphenol can be synthesized by the Friedel-Crafts acylation of phenol with acetyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride.
Industrial-Scale Production
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are both produced on a large scale for use in the production of a variety of products.
4-ethylphenol is used in the production of fragrances, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
p-ethylphenol is used in the production of antioxidants, dyes, and rubber.
Factors Affecting Yield and Purity
The yield and purity of 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol can be affected by a number of factors, including the reaction temperature, the reaction time, the catalyst used, and the presence of impurities.
Applications and Uses
Pharmaceuticals
4-ethylphenol is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib.
p-ethylphenol is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of a variety of antibiotics, including penicillin and erythromycin.
Fragrances, Draw 4 ethylphenol p ethylphenol
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are both used as fragrance ingredients in a variety of products, including perfumes, colognes, and soaps.
Plastics
4-ethylphenol is used as an antioxidant in the production of plastics.
p-ethylphenol is used as a plasticizer in the production of plastics.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Environmental Impact
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are both toxic to aquatic organisms.
They can also bioaccumulate in the food chain.
Toxicity and Hazards to Human Health
4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol are both toxic to humans.
They can cause skin irritation, eye irritation, and respiratory problems.
Regulations and Guidelines
There are a number of regulations and guidelines in place to protect human health and the environment from the harmful effects of 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol.
These regulations and guidelines include limits on the levels of these compounds that are allowed in drinking water, air, and soil.
FAQ Corner
What are the key differences between 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol?
While both compounds share the same molecular formula, their structural isomers result in distinct properties. 4-ethylphenol features an ethyl group at the fourth carbon atom of the benzene ring, whereas p-ethylphenol has its ethyl group attached to the para position, directly opposite the hydroxyl group.
How are 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol synthesized?
Several methods exist for synthesizing these compounds, including the alkylation of phenol with ethyl chloride, the reduction of 4-ethylanisole, and the hydrolysis of 4-ethylphenyl acetate.
What are the primary applications of 4-ethylphenol and p-ethylphenol?
4-ethylphenol finds use as an intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and antioxidants. p-ethylphenol, on the other hand, is employed in the synthesis of dyes, plastics, and agrochemicals.