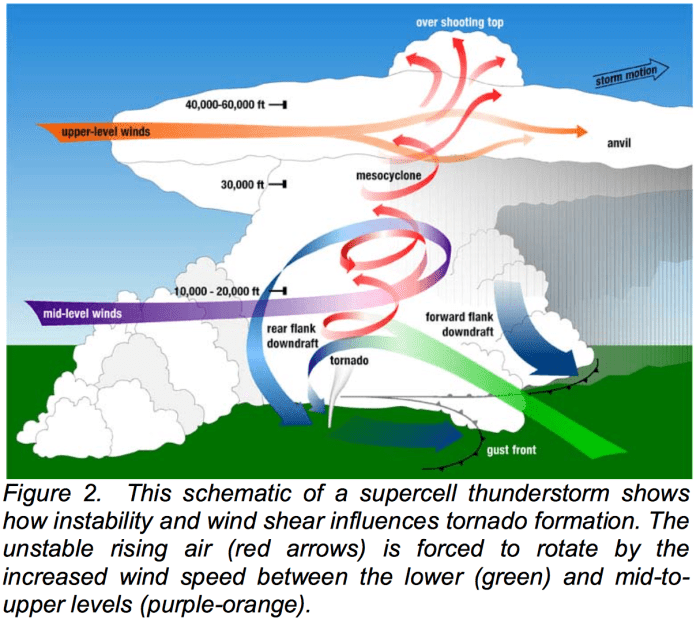
Tornadoes can negatively affect an ecosystem when they strike, causing widespread destruction and disrupting the delicate balance of nature. These powerful storms can destroy trees, alter soil structure, and contaminate water bodies, leading to a cascade of negative impacts on plant and animal life.
The impact of tornadoes on ecosystems is far-reaching, affecting everything from individual species to the overall health and productivity of the environment. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which tornadoes can negatively affect ecosystems, examining the mechanisms behind these impacts and discussing the potential long-term consequences.
Tornadoes and Ecosystem Disruption: Tornadoes Can Negatively Affect An Ecosystem When

Tornadoes, violent storms with rotating columns of air, can have devastating effects on ecosystems. Their high winds and debris can cause widespread destruction, disrupting habitats, killing species, and altering nutrient cycles.
Habitat Disruption
Tornadoes can destroy trees, depriving animals of shelter and nesting sites. They can also alter soil structure, affecting vegetation growth and animal habitats. Water bodies may be disrupted, affecting fish populations and aquatic ecosystems.
Species Mortality
Tornadoes can cause significant mortality among animal species. Wind speed, debris impact, and habitat loss contribute to animal deaths. Mortality rates vary depending on the species, with some being more vulnerable than others.
Nutrient Cycling
Tornadoes can disrupt nutrient cycles by removing vegetation and altering soil composition. Nutrient loss can reduce ecosystem productivity and sustainability, affecting the availability of nutrients for plants and animals.
Soil Erosion, Tornadoes can negatively affect an ecosystem when
Tornadoes can cause soil erosion through wind and water action. This can reduce soil fertility, water quality, and plant growth, with potential long-term effects on ecosystem health and agricultural productivity.
Water Quality
Tornadoes can contaminate water bodies with debris, sediment, and chemicals. Water pollution can harm aquatic life, human health, and ecosystem services, such as fishing and recreation.
Succession and Recovery
After a tornado, ecological succession occurs as the ecosystem recovers. The rate and trajectory of recovery depend on factors such as the severity of the damage, the resilience of the species, and environmental conditions. Long-term changes in ecosystem composition and function are possible.
FAQ Resource
How do tornadoes affect animal populations?
Tornadoes can kill animals directly through wind shear, debris impact, or habitat loss. They can also disrupt food chains and alter predator-prey relationships, leading to long-term changes in animal populations.
What is the impact of tornadoes on soil health?
Tornadoes can erode topsoil, remove nutrients, and alter soil structure, reducing soil fertility and productivity. This can have negative consequences for plant growth and the overall health of the ecosystem.
How do tornadoes affect water quality?
Tornadoes can contaminate water bodies with debris, sediment, and chemicals, leading to water pollution. This can harm aquatic life, disrupt ecosystem services, and pose a risk to human health.