Introducing the Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key iCivics, an authoritative guide to the fundamental principles and structure of the United States Constitution. This comprehensive resource provides a clear understanding of the document’s historical context, key provisions, and contemporary relevance, empowering individuals to engage with the foundational framework of American democracy.
Through engaging narratives and insightful explanations, this guide unravels the intricacies of the Constitution, fostering a deeper appreciation for its enduring impact on American society.
1. Introduction
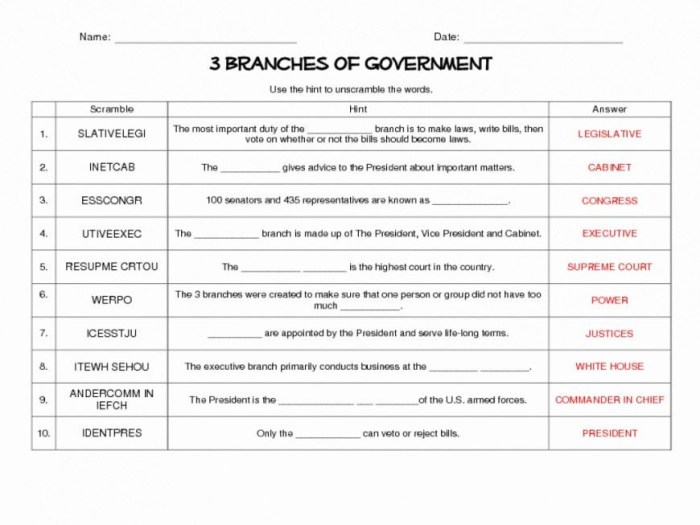
The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land, establishing the framework for the federal government and protecting the rights of individuals. The Anatomy of the Constitution answer key from iCivics provides a comprehensive guide to the document’s structure, key provisions, and historical context.
The Constitution serves as the foundation for the American political system, outlining the powers and responsibilities of the three branches of government (legislative, executive, and judicial), as well as the fundamental rights and freedoms of citizens.
2. Structure of the Constitution

Preamble, Anatomy of the constitution answer key icivics
The preamble to the Constitution is a concise statement of the document’s purpose, including establishing a more perfect union, securing the blessings of liberty, and promoting the general welfare.
Articles
The Constitution consists of seven articles, each addressing a specific aspect of government:
- Article I: Legislative Branch (Congress)
- Article II: Executive Branch (President)
- Article III: Judicial Branch (Courts)
- Article IV: States and Relations
- Article V: Amendment Process
- Article VI: Supremacy Clause
- Article VII: Ratification
Amendments
The Constitution has been amended 27 times since its ratification, with the first ten amendments known as the Bill of Rights. These amendments address various rights and freedoms, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to bear arms.
3. Key Concepts and Principles

Federalism
Federalism is the division of power between the national government and the states. The Constitution establishes a balance between the two, with the federal government having certain enumerated powers and the states retaining all other powers.
Separation of Powers
The Constitution divides the powers of government among three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. This separation of powers is designed to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights consists of the first ten amendments to the Constitution and guarantees certain fundamental rights and freedoms to individuals, including the right to a fair trial, freedom from unreasonable searches and seizures, and the right to due process of law.
4. Historical Context: Anatomy Of The Constitution Answer Key Icivics
Development
The Constitution was drafted by delegates to the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in 1787. The delegates debated various proposals and compromises before reaching a final agreement.
Ratification
The Constitution was ratified by the required number of states in 1788 and went into effect in 1789. The Federalist Papers, written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay, played a crucial role in persuading the public to support the ratification.
5. Application and Interpretation
Interpretation
The Supreme Court has the ultimate authority to interpret the Constitution. The Court’s decisions have shaped the application and understanding of the document throughout history.
Landmark Cases
Landmark Supreme Court cases such as Marbury v. Madison, Dred Scott v. Sandford, and Brown v. Board of Education have had a profound impact on constitutional law and American society.
6. Contemporary Relevance
Relevance
The Constitution remains a vital document in today’s society, providing the framework for the functioning of the government and the protection of individual rights.
Debates and Controversies
There are ongoing debates and controversies surrounding the Constitution, such as the scope of executive power, the role of the Supreme Court, and the interpretation of the Bill of Rights.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of the Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key iCivics?
The Anatomy of the Constitution Answer Key iCivics provides a comprehensive guide to the US Constitution, explaining its structure, key provisions, historical context, and contemporary relevance.
How does the guide explain the structure of the Constitution?
The guide describes the Preamble, seven Articles, and Amendments, highlighting their key provisions and the principles they embody.
What historical context does the guide provide?
The guide traces the development of the Constitution, including the debates and compromises that shaped the final document, as well as the ratification process.